Thottea grandiflora Rottboell
Common Name: Hempeduk Beruang (Jakun Tribe), Telingok Kelawar (Jakun Tribe), Bunga Semubut
Family: Aristolochiaceae
Description:
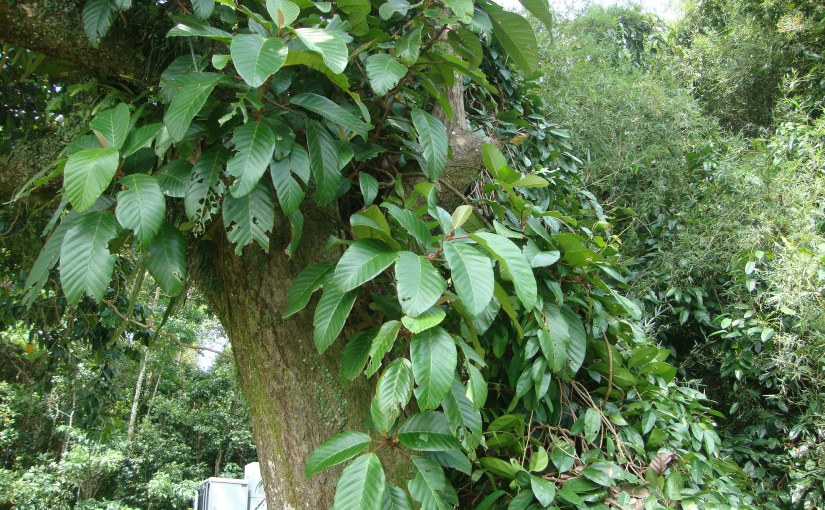
Growth Form: It is an erect shrub that can grow up to 2 m tall. Its branches are round and covered with fine hair.
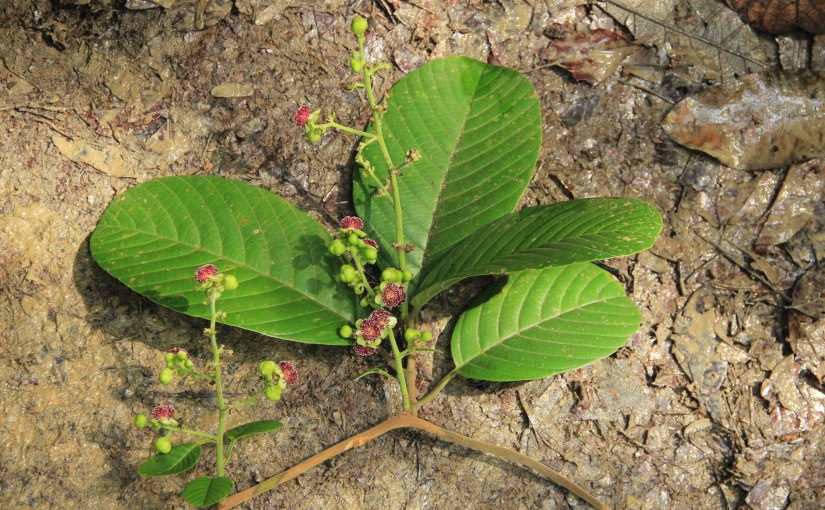
Foliage: The leaves are alternately arranged and stalked leaves have leathery leaf blades which are in drop-shaped, elliptic or lance-shaped. The size ranges from 15 to 45cm by 19 to 25cm.
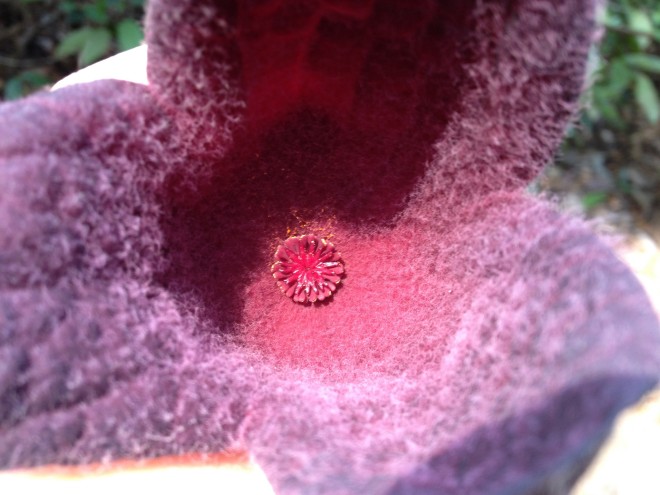
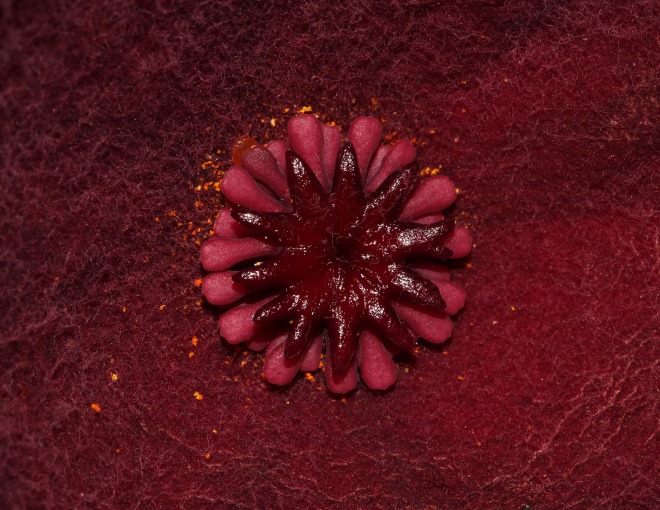
Flowers: The cluster of flowers are 1 to 7cm long and are usually found at the lower part of the stem. They are a funnel-shaped perianth with a deep red wine-coloured with some purple blotches.
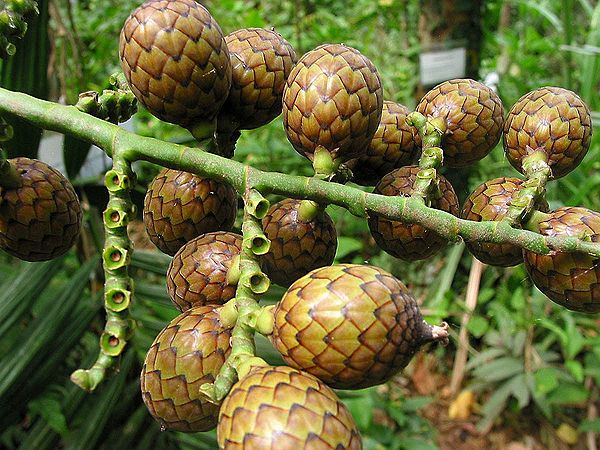
Fruits: The shape of the fruits are slender capsules that can size up to 15 cm long, and either straight or twisted. They are 4-angled and covered with hair. Its seeds are ellipsoid, 3-angled, with wrinkled surface.
Habit: Shrub
Habitat: It can be natively found in Myanmar, Peninsular Malaysia, and Singapore. It can grow in terrestrial environments such as primary rainforest, secondary rainforest and freshwater swamp forest.
Ethnobotanical Uses:
Plant Part Used: Root
Preparation Method: Decoction in water
Way of Administration: It can be orally consumed by drinking the decocted water of the roots.
Use to treat: The decocted water can be used to treat cough and asthma.
Reference
National Parks-Flora and Fauna Web (2013). Thottea grandiflora Rottboell. Retrieved at 28 May 2018. Available at https://florafaunaweb.nparks.gov.sg/Special-Pages/plant-detail.aspx?id=2508
Photograph
Credit to Ng C. (2017). Available at flickr.com